..
연결 리스트(Linked List)
Index
연결 리스트는 각 원소(node)가 데이터(data)와 함께, 다음 노드의 주소를 저장하는 방식의 자료구조이다
단일 연결 리스트
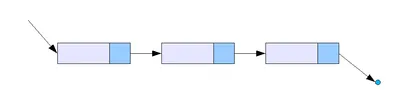
단일 연결 리스트는 각 노드가 자신의 데이터와 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터를 가지는 구조이다
이중 연결 리스트
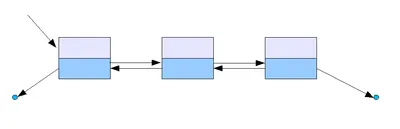
각 노드가 자신의 이전 원소와 다음 원소의 주소를 둘 다 들고 있다
각 노드가 prev와 next 두 개의 포인터를 가지므로, 단일 연결 리스트보다 노드 하나당 메모리 사용량이 많다
원형 연결 리스트
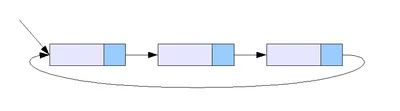
마지막 노드의 포인터가 첫 번째 노드를 가리키는 구조이다
단일 연결 리스트든, 이중 연결 리스트든 원형으로 만들 수 있다
코드 리뷰
단일 연결 리스트
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# 리스트 구성
head = Node(1)
second = Node(2)
third = Node(3)
head.next = second
second.next = third
# 출력
current = head
while current:
print(current.data, end=" -> ")
current = current.next
3가지의 노드들을 head -> second -> third로 연결한다
while문을 통해 current 값이 있을 동안 data 값을 출력하고
current의 다음 노드를 current로 만든다
이중 연결 리스트
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
# 리스트 구성
head = Node(1)
second = Node(2)
third = Node(3)
head.next = second
second.prev = head
second.next = third
third.prev = second
# 순방향 출력
current = head
while current:
print(current.data, end=" <-> ")
current = current.next
# 역방향 출력
current = third
while current:
print(current.data, end=" <-> ")
current = current.prev
Node 클래스에 self.prev = None만 추가되었다
각 노드에 prev와 next를 지정해준다
마지막에 prev을 이용하여 역방향 출력이 가능하다는 것을 보여준다
원형 연결 리스트
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# 리스트 구성
head = Node(1)
second = Node(2)
third = Node(3)
head.next = second
second.next = third
third.next = head # 원형 연결
# 순환 출력 (3번까지만)
current = head
count = 0
while count < 6:
print(current.data, end=" -> ")
current = current.next
count += 1
단일 연결 리스트로 원형 연결 리스트를 구현했다
마지막 노드의 next를 첫 노드로 연결하였다
노드의 삽입
new_node = Node(1.5)
new_node.next = second
head.next = new_node
new node의 next에 삽입할 위치 다음에 있는 노드를 지정한다
이전 노드인 head의 next를 new node로 지정한다
노드의 삭제
head.next = head.next.next
삭제 할 이전 노드의 next를 다다음 노드로 지정하여 중간 노드를 생략(삭제)한다
시간 복잡도
배열 vs 리스트
| 항목 | 배열 (Array) | 연결 리스트 (Linked List) |
|---|---|---|
| k번째 원소 접근 | O(1) (즉시 접근 가능) | O(k) (앞에서부터 순차 탐색) |
| 원소 추가/제거 | O(N) (요소 이동 필요) | O(1) (포인터만 수정) |
| 메모리 배치 | 연속적 메모리 공간 | 불연속적, 노드마다 동적 할당 |
| 오버헤드 (메모리) | 없음 | O(N) (포인터 공간 등 추가 비용 발생) |
C로 보는 단일 연결 리스트
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 노드 구조체 정의
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
// 새 노드 생성 함수
Node* createNode(int data) {
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (newNode == NULL) {
printf("메모리 할당 실패\n");
exit(1);
}
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// 리스트 앞에 노드 삽입
void insertFront(Node** head, int data) {
Node* newNode = createNode(data);
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
// 특정 값을 가진 노드 삭제
void deleteNode(Node** head, int key) {
Node* temp = *head;
Node* prev = NULL;
// 첫 노드가 삭제 대상인 경우
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
*head = temp->next;
free(temp);
return;
}
// 삭제할 노드 탐색
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// 값이 없는 경우
if (temp == NULL) return;
// 노드 삭제
prev->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
// 리스트 출력
void printList(Node* head) {
Node* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
printf("[%d] -> ", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// 메모리 해제
void freeList(Node* head) {
Node* current = head;
Node* nextNode;
while (current != NULL) {
nextNode = current->next;
free(current);
current = nextNode;
}
}
// 메인 함수
int main() {
Node* head = NULL;
insertFront(&head, 10);
insertFront(&head, 20);
insertFront(&head, 30);
printf("리스트 상태: ");
printList(head); // [30] -> [20] -> [10] -> NULL
printf("20 삭제 후: ");
deleteNode(&head, 20);
printList(head); // [30] -> [10] -> NULL
freeList(head); // 메모리 해제
return 0;
}