..
최소 신장 트리(MST)
신장 트리(Spanning Tree)는 그래프의 모든 정점을 포함하면서 사이클 없이 연결된 트리
최소 신장 트리(Minimum Spanning Tree)는 여러 개의 신장 트리 중에서 간선들의 가중치 합이 최소인 트리
무방향 그래프에서 정의됨
모든 정점을 연결하면서 사이클이 없어야 함
MST는 정점이 V개일 때 간선이 정확히 V - 1개인 트리를 생성
최소 비용으로 모든 정점을 연결하고 할 때 사용
MST는 트리다 → 트리는 간선이 V-1개 → MST도 정확히 V-1개만 필요하다
대표 알고리즘
크루스칼 알고리즘(Kruskal’s Algorithm)
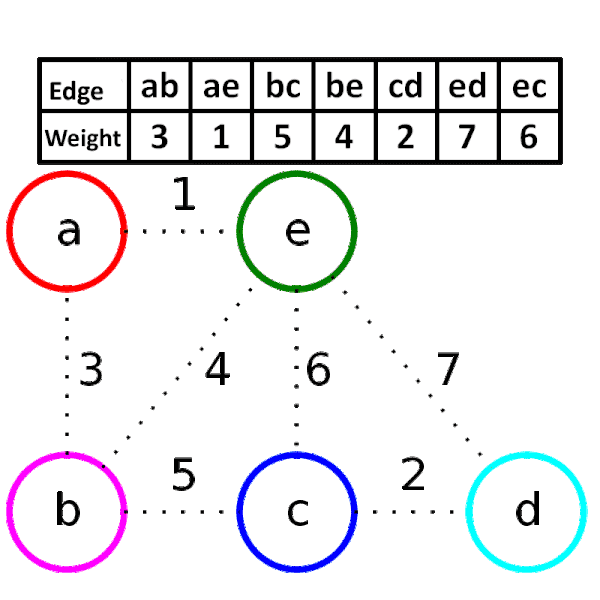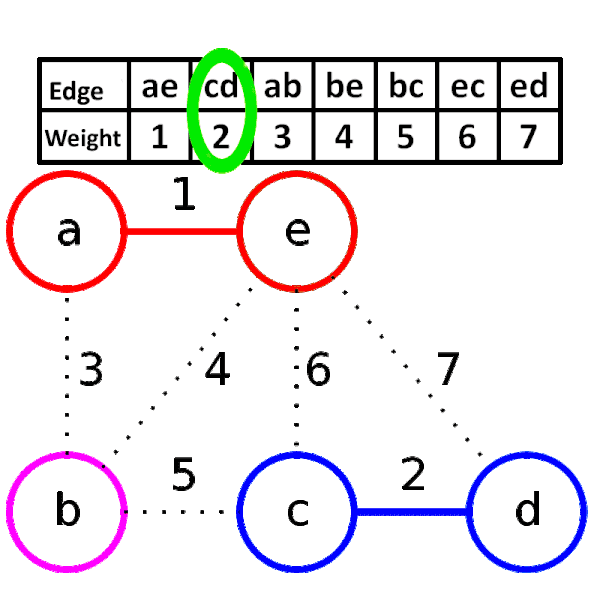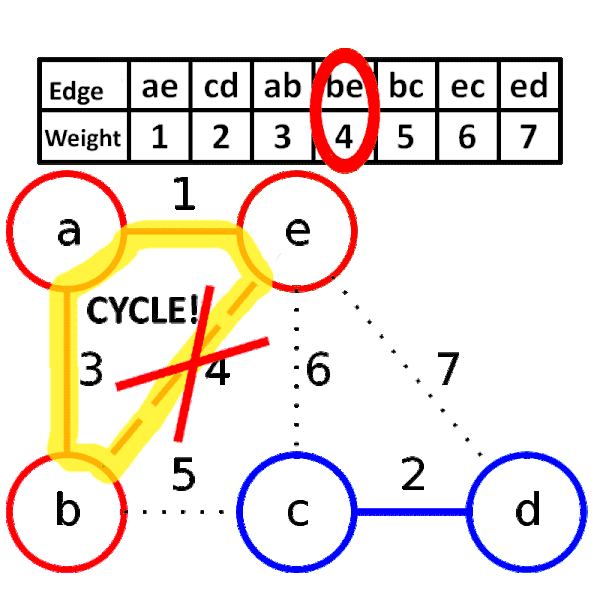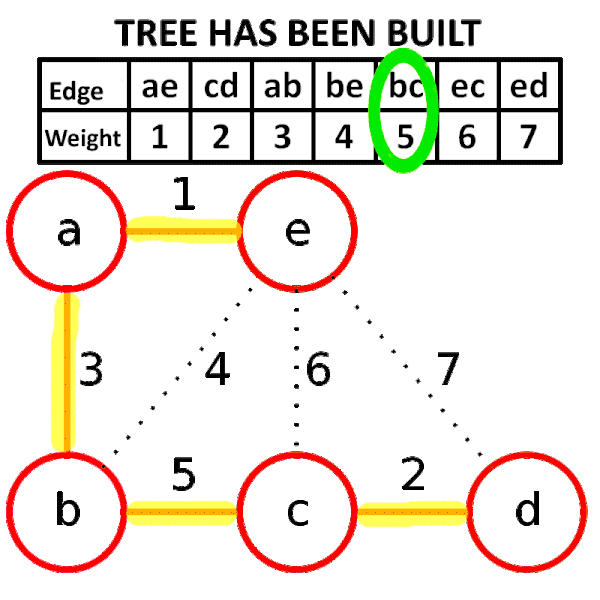
# 1. 유니온 파인드 구현
def find_parent(parent, x):
if parent[x] != x:
parent[x] = find_parent(parent, parent[x]) # 경로 압축
return parent[x]
def union_parent(parent, a, b):
a_root = find_parent(parent, a)
b_root = find_parent(parent, b)
if a_root < b_root:
parent[b_root] = a_root
else:
parent[a_root] = b_root
# 2. 입력 (정점 수, 간선 정보)
V = 5 # 정점 수
edges = [ # (가중치, 정점1, 정점2)
(1, 1, 2),
(3, 1, 3),
(2, 2, 3),
(5, 2, 4),
(4, 3, 4),
(6, 3, 5),
(7, 4, 5),
]
# 3. 크루스칼 알고리즘 수행
edges.sort() # 가중치 기준 정렬
parent = [i for i in range(V + 1)] # 유니온 파인드 초기화
total_weight = 0 # MST 총 비용
mst = [] # MST에 포함된 간선
for cost, a, b in edges:
if find_parent(parent, a) != find_parent(parent, b):
union_parent(parent, a, b)
total_weight += cost
mst.append((a, b, cost))
# 4. 결과 출력
print("MST 간선 목록:")
for a, b, cost in mst:
print(f"{a} - {b} (비용: {cost})")
print(f"\n총 비용: {total_weight}")
간선 정렬 기반
- 간선들을 가중치 기준으로 오름차순 정렬
- 사이클이 생기지 않도록 간선을 하나씩 선택
- 유니온-파인드 자료구조를 활용하여 사이클 여부 판별
시간 복잡도 : O(E log E)
프림 알고리즘(Prim’s Algorithm)
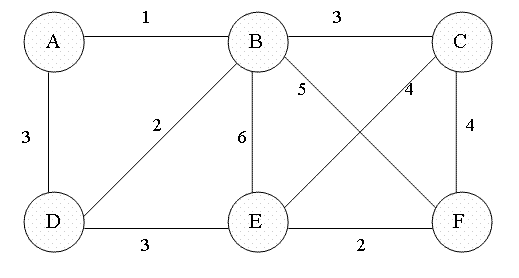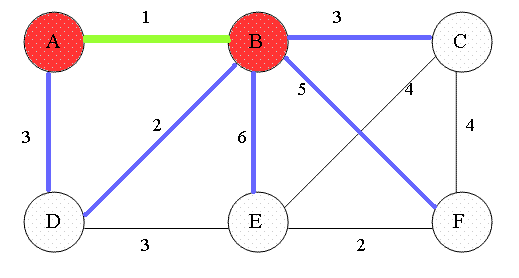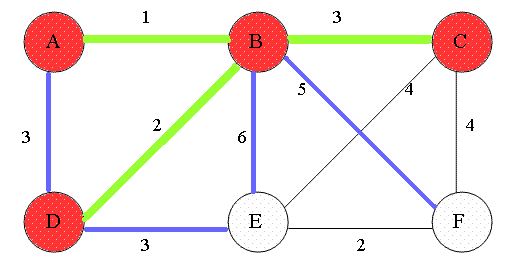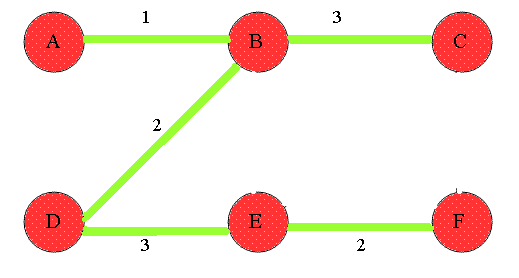
코드 리뷰
import heapq
def prim(graph, start):
visited = set()
min_heap = []
total_weight = 0
# 시작점에서 갈 수 있는 간선들을 힙에 넣음
visited.add(start)
for neighbor, weight in graph[start]:
heapq.heappush(min_heap, (weight, start, neighbor))
mst_edges = []
while min_heap and len(visited) < len(graph):
weight, u, v = heapq.heappop(min_heap)
if v in visited:
continue
visited.add(v)
total_weight += weight
mst_edges.append((u, v, weight))
for next_node, next_weight in graph[v]:
if next_node not in visited:
heapq.heappush(min_heap, (next_weight, v, next_node))
return total_weight, mst_edges
# 실행
graph = {
0: [(1, 1), (3, 4), (2, 3)],
1: [(0, 1), (2, 2)],
2: [(1, 2), (0, 3), (3, 5)],
3: [(0, 4), (2, 5)]
}
cost, edges = prim(graph, 0)
print("최소 스패닝 트리 비용:", cost)
print("선택된 간선들:")
for u, v, w in edges:
print(f"{u} - {v} (가중치 {w})")
정점 중심, 힙 사용
- 하나의 정점에서 시작하여, 가장 적은 비용의 간선을 선택해 확장
- 이미 선택된 정점들과 연결된 간선에서 가장 가중치가 낮은 것을 계속 선택
- 우선순위 큐(힙) + 인접 리스트 기반 구현 시 효율적
시간 복잡도 : O(E log V)
E : 간선 수
V : 정점 수